Want even more credit card numbers? Generate Credit Cards
MasterCard
- 5522 6496 3369 1268 5522 6496 3369 1268, CVC2:568, 07/28
- 5119 2551 2396 2844 5119 2551 2396 2844, CVC2:418, 04/30
- 5382 8537 0509 2038 5382 8537 0509 2038, CVC2:879, 05/30
- 5292 2933 8131 4704 5292 2933 8131 4704, CVC2:679, 04/30
- 5304 1822 0826 6328 5304 1822 0826 6328, CVC2:472, 01/30
VISA
- 4916 6991 9872 7608 4916 6991 9872 7608, CVV2:000, 02/28
- 4916 3340 3544 2514 4916 3340 3544 2514, CVV2:793, 04/28
- 4539 8541 2476 3634 4539 8541 2476 3634, CVV2:721, 12/31
- 4929 0590 9623 3156 4929 0590 9623 3156, CVV2:472, 04/30
- 4485 5877 7194 9726 4485 5877 7194 9726, CVV2:341, 12/28
What is a credit card?
A credit card is a small, plastic (or sometimes metal) card issued by banks or financial institutions that allows you to make purchases or withdraw cash without using your own money upfront. Each card has a unique number, expiration date, and security code. When you use a credit card, you’re essentially borrowing money from the issuer up to a certain credit limit, which is determined based on your credit history and financial profile.
How does a credit card work?
When you buy goods or services with a credit card, the card issuer pays the merchant on your behalf. At the end of each billing cycle, you receive a statement listing all your purchases, the total amount owed, the minimum payment due, and the payment due date. You can choose to pay the full balance or just the minimum amount. Any unpaid balance is carried over to the next month, and interest is charged on the remaining amount. Typical annual interest rates (APR) range from 10% to 30%, so it’s important to understand your card’s terms.
Benefits and features
Credit cards offer various features and benefits, such as:
- Rewards and points: Many cards provide cashback, reward points, airline miles, or discounts on specific categories like groceries, dining, or travel.
- Purchase protection: Credit cards often offer protections against unauthorized transactions and may provide extended warranties or insurance on purchases.
- Convenience and global acceptance: Credit cards are widely accepted worldwide, making them useful for travel and online shopping.
- Building credit history: Responsible use of a credit card helps you build a positive credit history, which is important for future loans or mortgages.
Costs and fees
Some credit cards charge an annual fee, while others are free. Additional fees may include late payment fees, cash advance fees, foreign transaction fees, and over-limit fees. It’s important to review all potential charges before choosing a card.
How credit card companies make money
Credit card issuers earn revenue in several ways:
- Interest charges: When users carry a balance from month to month.
- Annual and late fees: Charged to cardholders.
- Merchant fees: Retailers pay a percentage of each sale made with a credit card.
Responsible use
While credit cards offer many benefits, it’s important to use them responsibly. Carrying high balances or missing payments can lead to debt, high interest charges, and damage to your credit score. Always read the terms and conditions, keep track of your spending, and aim to pay your balance in full whenever possible.
Anatomy of a credit card?

Front of a Credit Card

Back of a Credit Card
- Logo of the Issuing Bank
- EMV chip
- Hologram
- Credit Card Number
- Credit Card Network Logo
- Date of Expiry
- Name of Card Holder
- NFC Chip (Contactless)
- Magnetic Strip
- Card Holder's Signature
- "Card Not Present" Security Code
What are Credit Card Security Codes?
Below is the information about various Cards and the location of the security code:
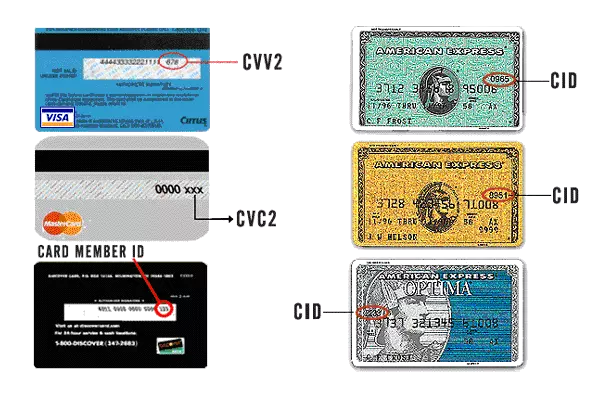
Credit cards use various types of security codes like CVC2, CVV2, CID, and CSC. MasterCard uses CVC2 and Visa uses CVV2, Discover and Amex uses CID (card identification number) and Debit Cards use CSC (card security code).
Credit Card Fraud
There are different types of credit card frauds that can leave the user in trouble. We hope the below information is useful to you:
- Stolen Cards - As the name suggests, the card holder is robbed of the card physically or card is poached from the mail before it reaches the card holder. User can immediately get the card cancelled by intimating the issuer company.
- Duplicated Cards - Merchants put the credit card in a secondary machine for copying it. These machines are easily available as they are multi-purpose.
- Application Fraud - This is similar to identification theft where a person files in the information of another person into the form using stolen or fake documents.
- Account Takeover - the fraudulent person requests a change of address by using genuine card holders personal information and then at a later date reports that the credit card was stolen. The new card will be mailed to the new address and will be used by the thief.
- Skimming - Payment receipts or account number or the security code of the credit card is copied to be used at a later time.
- Carding - In this process the card is not used but its number is used to verify its validity.. Using devices like generators (hopefully not mine) the thief enters the card information on any site that uses real-time processing of transactions. If the purchase is successful it means the card is still good, and is sold off to other individuals who will perform the fraud. Typical price range for these cards is upwards of $50 dollars per card.
Validation
Credit cards, debit cards along with gift cards and store cards all have a PAN (primary account number) and are created using the ISO/IEC 7812 standard. The number used is made up of four parts.
- Major Industry Identifier (MII) - this is the first digit of the PAN; Industries listed are Airlines, Travel, Banking, Petro, Helthcare, and Merchandising.
- Issuer Identifier Number (IINS) - the first six digits of a card number including the MII.
- The account number starts from the seventh digit to the second last digit, and can contain a maximum of 12 digits. The company issuing the card creates this number.
- The final digit is a check digit which can be figured out using Luhn's algorithm. If you want to learn more about the validation of credit cards check out Credit Card Validation.


